在此系列教程中,你将生成一个数学测验。 测验包含四个随机数学问题,测验者尝试在指定时间内回答。
控件使用 C# 或 Visual Basic 代码。 在本第二个教程中,通过添加基于随机数的数学问题代码,使测验具有挑战性。 还会创建一个名为 StartTheQuiz() 的方法来填充问题。
在本第二个教程中,你将了解如何:
- 编写代码以创建随机对象以用于数学问题。
- 为“开始”按钮添加事件处理程序。
- 编写代码以启动测验。
先决条件
本教程基于前面的教程,创建数学测验 WinForms 应用。 如果尚未完成该教程,请先完成该教程。
创建随机加法问题
在 Visual Studio 项目中,选择 Windows 窗体设计器。
选择窗体“Form1”。
在菜单栏上,选择“视图”>“代码”。 将显示 Form1.cs 或 Form1.vb,具体取决于使用的编程语言,以便可以查看表单背后的代码。
通过在 Form1.cs 或 Form1.vb中的代码顶部附近添加
new语句来创建 Random 对象。
可以像这样使用 new 语句来创建按钮、标签、面板、OpenFileDialogs、ColorDialogs、SoundPlayers、Randoms,甚至窗体。 这些项被称为 对象。
运行程序时,窗体将启动。 其背后的代码将创建一个 Random 对象,并将其命名为 randomizer。
测验需要变量来存储它为每个问题创建的随机数。 在使用变量之前,请声明它们,这意味着列出它们的名称和数据类型。
将两个整型变量添加到窗体,并在 Form1.cs 或 Form1.vb 中将它们分别命名为“addend1”和“addend2”。
说明
整数变量称为 C# 中的 int 或 Visual Basic 中的 整数。 这种变量存储从 -2147483648 到 2147483647 的正数或负数,并且只能存储整数,不能存储小数。
使用类似的语法添加整数变量,就像添加 Random 对象一样,如以下代码所示。
添加名为
StartTheQuiz()Form1.cs 或 Form1.vb的方法。 此方法使用 Random 对象的 Next() 方法为标签生成随机数。StartTheQuiz()最终将填写所有问题,然后启动计时器,因此请将此信息添加到摘要注释。 该函数应类似于以下代码。/// <summary> /// Start the quiz by filling in all of the problems /// and starting the timer. /// </summary> public void StartTheQuiz() { // Fill in the addition problem. // Generate two random numbers to add. // Store the values in the variables 'addend1' and 'addend2'. addend1 = randomizer.Next(51); addend2 = randomizer.Next(51); // Convert the two randomly generated numbers // into strings so that they can be displayed // in the label controls. plusLeftLabel.Text = addend1.ToString(); plusRightLabel.Text = addend2.ToString(); // 'sum' is the name of the NumericUpDown control. // This step makes sure its value is zero before // adding any values to it. sum.Value = 0; }
将 Next() 方法用于 Random 对象(例如调用 randomizer.Next(51)时),将获得小于 51 或介于 0 和 50 之间的随机数。 此代码调用 randomizer.Next(51),使两个随机数相加的结果介于 0 到 100 之间。
仔细看看这些语句。
这些语句设置 plusLeftLabel 和 plusRightLabel 的 Text 属性,以便它们显示两个随机数。 标签控件以文本格式显示值,在编程中,字符串保存文本。 每个整数的 ToString() 方法将整数转换为标签可以显示的文本。
创建随机减法、乘法和除法问题
下一步是声明变量并为其他数学问题提供随机值。
在加法题变量后,向窗体中添加其余数学题的整数变量。 Form1.cs 或 Form1.vb 中的代码应如以下示例所示。
public partial class Form1 : Form { // Create a Random object called randomizer // to generate random numbers. Random randomizer = new Random(); // These integer variables store the numbers // for the addition problem. int addend1; int addend2; // These integer variables store the numbers // for the subtraction problem. int minuend; int subtrahend; // These integer variables store the numbers // for the multiplication problem. int multiplicand; int multiplier; // These integer variables store the numbers // for the division problem. int dividend; int divisor;
通过添加以下代码,从“填写减法问题”注释开始,修改 Form1.cs 或 Form1.vb 中的
StartTheQuiz()方法。/// <summary> /// Start the quiz by filling in all of the problem /// values and starting the timer. /// </summary> public void StartTheQuiz() { // Fill in the addition problem. // Generate two random numbers to add. // Store the values in the variables 'addend1' and 'addend2'. addend1 = randomizer.Next(51); addend2 = randomizer.Next(51); // Convert the two randomly generated numbers // into strings so that they can be displayed // in the label controls. plusLeftLabel.Text = addend1.ToString(); plusRightLabel.Text = addend2.ToString(); // 'sum' is the name of the NumericUpDown control. // This step makes sure its value is zero before // adding any values to it. sum.Value = 0; // Fill in the subtraction problem. minuend = randomizer.Next(1, 101); subtrahend = randomizer.Next(1, minuend); minusLeftLabel.Text = minuend.ToString(); minusRightLabel.Text = subtrahend.ToString(); difference.Value = 0; // Fill in the multiplication problem. multiplicand = randomizer.Next(2, 11); multiplier = randomizer.Next(2, 11); timesLeftLabel.Text = multiplicand.ToString(); timesRightLabel.Text = multiplier.ToString(); product.Value = 0; // Fill in the division problem. divisor = randomizer.Next(2, 11); int temporaryQuotient = randomizer.Next(2, 11); dividend = divisor * temporaryQuotient; dividedLeftLabel.Text = dividend.ToString(); dividedRightLabel.Text = divisor.ToString(); quotient.Value = 0;
此代码在 Random 类的 Next() 方法的使用方式上与加法题略有不同。 为 Next() 方法两个值提供时,它会选取一个大于或等于第一个值的随机数,小于第二个值。
通过使用具有两个参数的 Next() 方法,可以确保减法问题有正答案,乘法答案最多为 100,除法答案不是分数。
将事件处理程序添加到“开始”按钮
在本部分中,将添加代码,以在选择“开始”按钮时启动测验。 响应按钮选择之类的事件时运行的代码称为事件处理程序。
在 Windows 窗体设计器中,双击 启动测验 按钮,或选中它,然后选择 输入。 此时将显示窗体的代码,并显示新方法。
这些操作将向“开始”按钮添加一个 Click 事件处理程序。 当测验参与者选择此按钮时,应用将运行您将添加到此新方法中的代码。
添加以下两个语句,以便事件处理程序启动测验。
第一个语句调用新的 StartTheQuiz() 方法。 第二个语句将 startButton 控件的 Enabled 属性设置为 false,以便测验接受者无法在测验过程中选择按钮。
运行应用
保存代码。
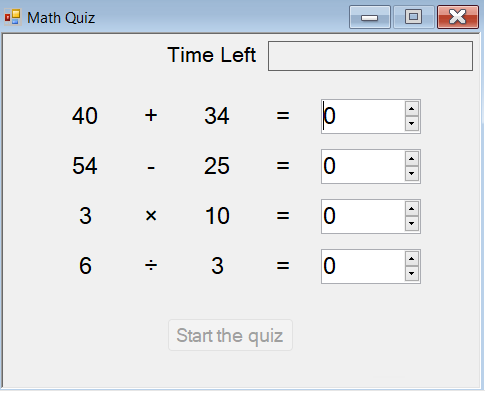
运行应用,然后选择 开始测验。 将显示随机数学问题,如以下屏幕截图所示。
后续步骤
转到下一教程,将计时器添加到数学测验并检查用户答案。