可区分联合提供对下面这种值的支持:该值可以是一些已命名用例中的一个,且每个用例可能具有不同的值和类型。 区分联合体对异类数据很有用;可以处理具有特殊情况的数据,包括有效案例和错误情况;数据类型从一个实例到另一个实例有所不同;也可以作为小型对象层次结构的替代方法。 此外,递归区分联合用于表示树数据结构。
语法
[ attributes ]
type [accessibility-modifier] type-name =
| case-identifier1 [of [ fieldname1 : ] type1 [ * [ fieldname2 : ] type2 ...]
| case-identifier2 [of [fieldname3 : ]type3 [ * [ fieldname4 : ]type4 ...]
[ member-list ]
言论
可区分联合类似于其他语言中的联合类型,但存在一些差异。 与 C++ 中的联合类型或 Visual Basic 中的变体类型一样,存储在值中的数据不是固定的;它可以是几种不同选项之一。 但是与其他这些语言中的联合不同,会向每个可能选项提供一个用例标识符。 用例标识符是此类型的对象可以具有的各种可能类型的值的名称;值是可选的。 如果值不存在,则事例等效于枚举事例。 如果存在值,则每个值可以是指定类型的单个值,也可以是聚合相同或不同类型的多个字段的元组。 可以为单个字段提供名称,但该名称是可选的(即使对相同用例中的其他字段进行了命名)。
可区分联合的可访问性默认为 public。
例如,请考虑以下 Shape 类型声明。
type Shape =
| Rectangle of width : float * length : float
| Circle of radius : float
| Prism of width : float * float * height : float
前面的代码声明一个区分的联合形状,该形状可以包含三种情况中的任意值:矩形、圆和 Prism。 每个用例都有一组不同的字段。 Rectangle 用例有两个命名字段,都属于类型 float,名称分别为 width 和 length。 Circle 用例只有一个命名字段 radius。 Prism 用例有三个字段,其中两个字段(width 和 height)为命名字段。 未命名字段称为匿名字段。
通过根据以下示例为命名字段和匿名字段提供值来构造对象。
let rect = Rectangle(length = 1.3, width = 10.0)
let circ = Circle (1.0)
let prism = Prism(5., 2.0, height = 3.0)
此代码展示了您可以在初始化中使用命名字段,也可以依照声明中字段的排序,依次为每个字段提供值。 上一代码中 rect 的构造函数调用使用命名字段,但 circ 的构造函数调用使用排序。 可以混合使用排序字段和命名字段,如 prism 的构造中所示。
option 类型是 F# 核心库中的简单判别联合体。 option 类型声明如下。
// The option type is a discriminated union.
type Option<'a> =
| Some of 'a
| None
前面的代码指定类型 Option 是一个区分的联合,有两种情况,Some 和 None。 Some 事例具有一个关联值,该值由一个匿名字段组成,该字段的类型由类型参数 'a表示。 None 用例没有关联值。 因此,option 类型指定具有某种类型的值或无值的泛型类型。 类型 Option 也有一个小写类型别名,option,更常用。
事例标识符可用作区分联合类型的构造函数。 例如,以下代码用于创建 option 类型的值。
let myOption1 = Some(10.0)
let myOption2 = Some("string")
let myOption3 = None
事例标识符也用于模式匹配表达式。 在模式匹配表达式中,将为与各个事例关联的值提供标识符。 例如,在以下代码中,x 是标识与 option 类型的 Some 情况相关的值的标识符。
let printValue opt =
match opt with
| Some x -> printfn "%A" x
| None -> printfn "No value."
在模式匹配表达式中,可以使用命名字段指定可区分联合匹配项。 对于之前声明的 Shape 类型,可以如以下代码所示使用命名字段提取字段的值。
let getShapeWidth shape =
match shape with
| Rectangle(width = w) -> w
| Circle(radius = r) -> 2. * r
| Prism(width = w) -> w
通常,使用用例标识符时可以无需使用联合名称来限定它们。 如果希望始终使用联合的名称来限定名称,则可将 RequireQualifiedAccess 属性应用于联合类型定义。
展开可区分联合
在 F# 中,可区分联合通常在域建模中用于展开单一类型。 也可以通过模式匹配轻松提取基础值。 无需对单个事例使用匹配表达式:
let ([UnionCaseIdentifier] [values]) = [UnionValue]
以下示例演示了这一点:
type ShaderProgram = | ShaderProgram of id:int
let someFunctionUsingShaderProgram shaderProgram =
let (ShaderProgram id) = shaderProgram
// Use the unwrapped value
...
函数参数中可以直接使用模式匹配,因此可以在其中解构单个情况:
let someFunctionUsingShaderProgram (ShaderProgram id) =
// Use the unwrapped value
...
结构可区分联合
还可以将可区分联合表示为结构。 这是使用 [<Struct>] 属性完成的。
[<Struct>]
type SingleCase = Case of string
[<Struct>]
type Multicase =
| Case1 of string
| Case2 of int
| Case3 of double
由于这些是值类型而不是引用类型,因此与引用可区分联合相比,有一些额外的注意事项:
- 它们被复制为值类型,并具有值类型语义。
- 不能将递归类型定义与多用例结构可区分联合一起使用。
在 F# 9 之前,每个案例都要求指定一个唯一的案例名称(在联合中)。 从 F# 9 开始,将解除限制。
使用可区分联合而不是对象层次结构
通常可以使用区分联合体,作为小型对象层次结构更简单的替代方法。 例如,可以使用以下可区分联合,而不是具有用于圆形、方形等的派生类型的 Shape 基类。
type Shape =
// The value here is the radius.
| Circle of float
// The value here is the side length.
| EquilateralTriangle of double
// The value here is the side length.
| Square of double
// The values here are the height and width.
| Rectangle of double * double
与在面向对象的实现中使用虚方法来计算面积或周长不同,你可以使用模式匹配来分支到适当的公式来计算这些量。 在下面的示例中,不同的公式用于计算区域,具体取决于形状。
let pi = 3.141592654
let area myShape =
match myShape with
| Circle radius -> pi * radius * radius
| EquilateralTriangle s -> (sqrt 3.0) / 4.0 * s * s
| Square s -> s * s
| Rectangle(h, w) -> h * w
let radius = 15.0
let myCircle = Circle(radius)
printfn "Area of circle that has radius %f: %f" radius (area myCircle)
let squareSide = 10.0
let mySquare = Square(squareSide)
printfn "Area of square that has side %f: %f" squareSide (area mySquare)
let height, width = 5.0, 10.0
let myRectangle = Rectangle(height, width)
printfn "Area of rectangle that has height %f and width %f is %f" height width (area myRectangle)
输出如下所示:
Area of circle that has radius 15.000000: 706.858347
Area of square that has side 10.000000: 100.000000
Area of rectangle that has height 5.000000 and width 10.000000 is 50.000000
对树数据结构使用可区分联合
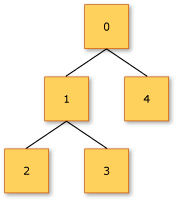
可区分联合可以是递归的,这意味着可将联合本身包含在一个或多个用例的类型中。 递归区分联合可用于创建树结构,这些结构用于在编程语言中为表达式建模。 在以下代码中,递归区分联合用于创建二进制树数据结构。 联合包括两个用例,即 Node(具有整数值以及左子树和右子树的节点)和 Tip(用于终止树)。
type Tree =
| Tip
| Node of int * Tree * Tree
let rec sumTree tree =
match tree with
| Tip -> 0
| Node(value, left, right) -> value + sumTree (left) + sumTree (right)
let myTree =
Node(0, Node(1, Node(2, Tip, Tip), Node(3, Tip, Tip)), Node(4, Tip, Tip))
let resultSumTree = sumTree myTree
在前面的代码中,resultSumTree 具有值 10。 下图显示了 myTree的树结构。
如果树中的节点是异类的,则可区分联合会十分有效。 在以下代码中,类型 Expression 表示一个简单编程语言中表达式的抽象语法树,该语言支持数字和变量的加法和乘法。 某些联合事例不是递归的,表示数字(Number)或变量(Variable)。 其他情况是递归的,表示作数(Add 和 Multiply),其中作数也是表达式。 Evaluate 函数使用匹配表达式以递归方式处理语法树。
type Expression =
| Number of int
| Add of Expression * Expression
| Multiply of Expression * Expression
| Variable of string
let rec Evaluate (env: Map<string, int>) exp =
match exp with
| Number n -> n
| Add(x, y) -> Evaluate env x + Evaluate env y
| Multiply(x, y) -> Evaluate env x * Evaluate env y
| Variable id -> env[id]
let environment = Map [ "a", 1; "b", 2; "c", 3 ]
// Create an expression tree that represents
// the expression: a + 2 * b.
let expressionTree1 = Add(Variable "a", Multiply(Number 2, Variable "b"))
// Evaluate the expression a + 2 * b, given the
// table of values for the variables.
let result = Evaluate environment expressionTree1
执行此代码时,result 的值为 5。
相互递归可区分联合
F# 中的可区分联合可以相互递归,这意味着多个联合类型可以以递归方式相互引用。 在对分层或互连结构进行建模时,这非常有用。 若要定义相互递归可区分联合,请使用 and 关键字。
例如,请考虑抽象语法树(AST)表示形式,其中表达式可以包含语句,语句可以包含表达式:
type Expression =
| Literal of int
| Variable of string
| Operation of string * Expression * Expression
and Statement =
| Assign of string * Expression
| Sequence of Statement list
| IfElse of Expression * Statement * Statement
成员
可以对可区分联合定义成员。 以下示例演示如何定义属性并实现接口:
open System
type IPrintable =
abstract Print: unit -> unit
type Shape =
| Circle of float
| EquilateralTriangle of float
| Square of float
| Rectangle of float * float
member this.Area =
match this with
| Circle r -> Math.PI * (r ** 2.0)
| EquilateralTriangle s -> s * s * sqrt 3.0 / 4.0
| Square s -> s * s
| Rectangle(l, w) -> l * w
interface IPrintable with
member this.Print () =
match this with
| Circle r -> printfn $"Circle with radius %f{r}"
| EquilateralTriangle s -> printfn $"Equilateral Triangle of side %f{s}"
| Square s -> printfn $"Square with side %f{s}"
| Rectangle(l, w) -> printfn $"Rectangle with length %f{l} and width %f{w}"
案例的 .Is* 属性
自 F# 9,可区分联合为每个案例公开自动生成的 .Is* 属性,使你能够检查某个值是否为特定案例。
这是如何使用它:
type Contact =
| Email of address: string
| Phone of countryCode: int * number: string
type Person = { name: string; contact: Contact }
let canSendEmailTo person =
person.contact.IsEmail // .IsEmail is auto-generated
常见属性
以下属性常常出现在可区分联合中:
[<RequireQualifiedAccess>][<NoEquality>][<NoComparison>][<Struct>]
