在本教程中,你将创建一个 MSTest 应用来评估 OpenAI 模型的聊天响应。 测试应用使用 Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation 库执行评估、缓存模型响应和创建报表。 本教程同时使用内置评估器和自定义评估器。 内置质量评估程序(来自 Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Quality 包)使用 LLM 执行评估;自定义计算器不使用 AI。
先决条件
配置 AI 服务
若要使用 Azure 门户预配 Azure OpenAI 服务和模型,请完成创建和部署 Azure OpenAI 服务资源一文中的步骤。 在“部署模型”步骤中,选择模型 gpt-4o 。
创建测试应用
完成以下步骤以创建连接到 gpt-4o AI 模型的 MSTest 项目。
在终端窗口中,导航到要在其中创建应用的目录,并使用
dotnet new以下命令创建新的 MSTest 应用:dotnet new mstest -o TestAIWithReporting导航到
TestAIWithReporting目录,并将必要的包添加到应用:dotnet add package Azure.AI.OpenAI dotnet add package Azure.Identity dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Abstractions dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Quality dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Reporting dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.AI.OpenAI --prerelease dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.UserSecrets运行以下命令,为 Azure OpenAI 终结点、模型名称和租户 ID 添加 应用机密 :
dotnet user-secrets init dotnet user-secrets set AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT <your-Azure-OpenAI-endpoint> dotnet user-secrets set AZURE_OPENAI_GPT_NAME gpt-4o dotnet user-secrets set AZURE_TENANT_ID <your-tenant-ID>(根据环境,可能不需要租户 ID。在这种情况下,请将其从实例化 DefaultAzureCredential 的代码中删除。)
在所选编辑器中打开新应用。
添加测试应用代码
将 Test1.cs 文件重命名为 MyTests.cs,然后打开该文件并将类重命名为
MyTests。 删除空TestMethod1方法。将必要的
using指令添加到文件顶部。using Azure.AI.OpenAI; using Azure.Identity; using Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation; using Microsoft.Extensions.AI; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Reporting.Storage; using Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Reporting; using Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Quality;将 TestContext 属性添加到类。
// The value of the TestContext property is populated by MSTest. public TestContext? TestContext { get; set; }添加
GetAzureOpenAIChatConfiguration方法,该方法创建IChatClient供计算器与模型通信。private static ChatConfiguration GetAzureOpenAIChatConfiguration() { IConfigurationRoot config = new ConfigurationBuilder().AddUserSecrets<MyTests>().Build(); string endpoint = config["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"]; string model = config["AZURE_OPENAI_GPT_NAME"]; string tenantId = config["AZURE_TENANT_ID"]; // Get an instance of Microsoft.Extensions.AI's <see cref="IChatClient"/> // interface for the selected LLM endpoint. AzureOpenAIClient azureClient = new( new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential(new DefaultAzureCredentialOptions() { TenantId = tenantId })); IChatClient client = azureClient.GetChatClient(deploymentName: model).AsIChatClient(); // Create an instance of <see cref="ChatConfiguration"/> // to communicate with the LLM. return new ChatConfiguration(client); }设置报告功能。
private string ScenarioName => $"{TestContext!.FullyQualifiedTestClassName}.{TestContext.TestName}"; private static string ExecutionName => $"{DateTime.Now:yyyyMMddTHHmmss}"; private static readonly ReportingConfiguration s_defaultReportingConfiguration = DiskBasedReportingConfiguration.Create( storageRootPath: "C:\\TestReports", evaluators: GetEvaluators(), chatConfiguration: GetAzureOpenAIChatConfiguration(), enableResponseCaching: true, executionName: ExecutionName);方案名称
方案名称设置为当前测试方法的完全限定名称。 但是,可以在调用 CreateScenarioRunAsync(String, String, IEnumerable<String>, IEnumerable<String>, CancellationToken)时将其设置为所选的任何字符串。 下面是选择方案名称的一些注意事项:
- 使用基于磁盘的存储时,方案名称用作存储相应评估结果的文件夹的名称。 因此,最好保持名称合理短,并避免在文件和目录名称中不允许的任何字符。
- 默认情况下,生成的评估报告拆分方案名称
.,以便结果可以在分层视图中显示,并具有适当的分组、嵌套和聚合。 在方案名称设置为相应测试方法的完全限定名称的情况下,这特别有用,因为它允许结果按层次结构中的命名空间和类名进行分组。 但是,还可以通过在自己的自定义方案名称中包含句点(.)来利用此功能,以创建最适合方案的报告层次结构。
执行名称
执行名称用于对存储评估结果时属于同一评估运行(或测试运行)的评估结果进行分组。 如果在创建 a ReportingConfiguration时未提供执行名称,则所有计算运行都将使用相同的默认执行名称
Default。 在这种情况下,一次运行的结果将被下一个运行覆盖,并且你失去了在不同运行中比较结果的能力。此示例使用时间戳作为执行名称。 如果项目中有多个测试,请确保在测试中使用的所有报告配置中使用相同的执行名称来正确分组结果。
在更实际的应用场景中,你可能还希望在多个不同程序集中的评估测试之间共享相同的执行名称,而这些测试是在不同的测试进程中运行的。 在这种情况下,可以在运行测试之前使用脚本更新具有适当执行名称的环境变量(例如 CI/CD 系统分配的当前内部版本号)。 或者,如果您的构建系统生成单调递增的程序集文件版本,您可以从测试代码中读取 AssemblyFileVersionAttribute,然后将其用作执行名称,以比较不同产品版本的结果。
报告配置
- 通过调用 ScenarioRun 创建的每个 CreateScenarioRunAsync(String, String, IEnumerable<String>, IEnumerable<String>, CancellationToken) 应调用的评估器集。
- 计算器应该使用的 LLM 终结点(请参阅 ReportingConfiguration.ChatConfiguration)。
- 应存储方案运行结果的方式和位置。
- 如何缓存与方案运行相关的 LLM 响应。
- 报告方案运行结果时应使用的执行名称。
此测试使用基于磁盘的报告配置。
在单独的文件中,添加
WordCountEvaluator类,该类是实现的 IEvaluator自定义计算器。using System.Text.RegularExpressions; using Microsoft.Extensions.AI; using Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation; namespace TestAIWithReporting; public class WordCountEvaluator : IEvaluator { public const string WordCountMetricName = "Words"; public IReadOnlyCollection<string> EvaluationMetricNames => [WordCountMetricName]; /// <summary> /// Counts the number of words in the supplied string. /// </summary> private static int CountWords(string? input) { if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(input)) { return 0; } MatchCollection matches = Regex.Matches(input, @"\b\w+\b"); return matches.Count; } /// <summary> /// Provides a default interpretation for the supplied <paramref name="metric"/>. /// </summary> private static void Interpret(NumericMetric metric) { if (metric.Value is null) { metric.Interpretation = new EvaluationMetricInterpretation( EvaluationRating.Unknown, failed: true, reason: "Failed to calculate word count for the response."); } else { if (metric.Value <= 100 && metric.Value > 5) metric.Interpretation = new EvaluationMetricInterpretation( EvaluationRating.Good, reason: "The response was between 6 and 100 words."); else metric.Interpretation = new EvaluationMetricInterpretation( EvaluationRating.Unacceptable, failed: true, reason: "The response was either too short or greater than 100 words."); } } public ValueTask<EvaluationResult> EvaluateAsync( IEnumerable<ChatMessage> messages, ChatResponse modelResponse, ChatConfiguration? chatConfiguration = null, IEnumerable<EvaluationContext>? additionalContext = null, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default) { // Count the number of words in the supplied <see cref="modelResponse"/>. int wordCount = CountWords(modelResponse.Text); string reason = $"This {WordCountMetricName} metric has a value of {wordCount} because " + $"the evaluated model response contained {wordCount} words."; // Create a <see cref="NumericMetric"/> with value set to the word count. // Include a reason that explains the score. var metric = new NumericMetric(WordCountMetricName, value: wordCount, reason); // Attach a default <see cref="EvaluationMetricInterpretation"/> for the metric. Interpret(metric); return new ValueTask<EvaluationResult>(new EvaluationResult(metric)); } }WordCountEvaluator计算响应中存在的单词数。 与某些评估程序不同,它不基于 AI。EvaluateAsync方法返回一个 EvaluationResult,其中包含一个包含字数的 NumericMetric。该方法
EvaluateAsync还会将默认解释附加到指标上。 如果检测到的字数计数介于 6 到 100 之间,则默认解释将指标视为良好(可接受的)。 否则,该指标被视为失败。 如果需要,调用方可以覆盖此默认解释。返回
MyTests.cs,添加一个方法来收集评估器,以便在评估中使用。private static IEnumerable<IEvaluator> GetEvaluators() { IEvaluator relevanceEvaluator = new RelevanceEvaluator(); IEvaluator coherenceEvaluator = new CoherenceEvaluator(); IEvaluator wordCountEvaluator = new WordCountEvaluator(); return [relevanceEvaluator, coherenceEvaluator, wordCountEvaluator]; }添加方法以添加系统提示 ChatMessage、定义 聊天选项,并询问模型以响应给定的问题。
private static async Task<(IList<ChatMessage> Messages, ChatResponse ModelResponse)> GetAstronomyConversationAsync( IChatClient chatClient, string astronomyQuestion) { const string SystemPrompt = """ You're an AI assistant that can answer questions related to astronomy. Keep your responses concise and under 100 words. Use the imperial measurement system for all measurements in your response. """; IList<ChatMessage> messages = [ new ChatMessage(ChatRole.System, SystemPrompt), new ChatMessage(ChatRole.User, astronomyQuestion) ]; var chatOptions = new ChatOptions { Temperature = 0.0f, ResponseFormat = ChatResponseFormat.Text }; ChatResponse response = await chatClient.GetResponseAsync(messages, chatOptions); return (messages, response); }本教程中的测试评估 LLM 对天文学问题的响应。 由于启用了响应缓存,并且由于提供的ReportingConfiguration总是从使用此报告配置创建的IChatClient中获取,因此测试的LLM响应被缓存并重复使用。 响应将重复使用,直到相应的缓存条目过期(默认为 14 天),或者直到任何请求参数(如 LLM 终结点或被问的问题)更改。
添加用于验证响应的方法。
/// <summary> /// Runs basic validation on the supplied <see cref="EvaluationResult"/>. /// </summary> private static void Validate(EvaluationResult result) { // Retrieve the score for relevance from the <see cref="EvaluationResult"/>. NumericMetric relevance = result.Get<NumericMetric>(RelevanceEvaluator.RelevanceMetricName); Assert.IsFalse(relevance.Interpretation!.Failed, relevance.Reason); Assert.IsTrue(relevance.Interpretation.Rating is EvaluationRating.Good or EvaluationRating.Exceptional); // Retrieve the score for coherence from the <see cref="EvaluationResult"/>. NumericMetric coherence = result.Get<NumericMetric>(CoherenceEvaluator.CoherenceMetricName); Assert.IsFalse(coherence.Interpretation!.Failed, coherence.Reason); Assert.IsTrue(coherence.Interpretation.Rating is EvaluationRating.Good or EvaluationRating.Exceptional); // Retrieve the word count from the <see cref="EvaluationResult"/>. NumericMetric wordCount = result.Get<NumericMetric>(WordCountEvaluator.WordCountMetricName); Assert.IsFalse(wordCount.Interpretation!.Failed, wordCount.Reason); Assert.IsTrue(wordCount.Interpretation.Rating is EvaluationRating.Good or EvaluationRating.Exceptional); Assert.IsFalse(wordCount.ContainsDiagnostics()); Assert.IsTrue(wordCount.Value > 5 && wordCount.Value <= 100); }小窍门
每个指标都包含一个
Reason属性,用于解释分数的原因。 原因包含在 生成的报表 中,可以通过单击相应指标卡片上的信息图标来查看。最后,添加 测试方法 本身。
[TestMethod] public async Task SampleAndEvaluateResponse() { // Create a <see cref="ScenarioRun"/> with the scenario name // set to the fully qualified name of the current test method. await using ScenarioRun scenarioRun = await s_defaultReportingConfiguration.CreateScenarioRunAsync( ScenarioName, additionalTags: ["Moon"]); // Use the <see cref="IChatClient"/> that's included in the // <see cref="ScenarioRun.ChatConfiguration"/> to get the LLM response. (IList<ChatMessage> messages, ChatResponse modelResponse) = await GetAstronomyConversationAsync( chatClient: scenarioRun.ChatConfiguration!.ChatClient, astronomyQuestion: "How far is the Moon from the Earth at its closest and furthest points?"); // Run the evaluators configured in <see cref="s_defaultReportingConfiguration"/> against the response. EvaluationResult result = await scenarioRun.EvaluateAsync(messages, modelResponse); // Run some basic validation on the evaluation result. Validate(result); }此测试方法:
创建 ScenarioRun。 使用
await using可确保ScenarioRun被正确处理,并且将此评估的结果正确保存到结果存储中。获取 LLM 对某个特定天文学问题的回答。 将用于评估的相同 IChatClient 值传递给
GetAstronomyConversationAsync方法,以便获取正在评估的主要 LLM 响应的 响应缓存 。 (此外,这还为 LLM 轮次启用了响应缓存,评估器使用 LLM 轮次在内部执行评估。)使用响应缓存,LLM 响应可以通过以下方式获取:- 直接在当前测试的首次运行中从 LLM 终结点获取,或者在后续运行中,如果缓存条目已过期(默认情况下为 14 天)。
- 在后续测试运行中,从
s_defaultReportingConfiguration中配置的(基于磁盘的)响应缓存中获取。
针对响应运行评估器。 与 LLM 响应一样,在随后的运行中,评估是从配置的
s_defaultReportingConfiguration(基于磁盘)的响应缓存中提取的。对评估结果进行一些基本验证。
此步骤是可选的,主要用于演示目的。 在实际评估中,你可能不想验证单个结果,因为随着产品(和所使用的模型)的发展,LLM 响应和评估分数可能会随着时间推移而变化。 如果发生这种情况,你可能不希望单个评估测试“失败”并因此阻止 CI/CD 流水线的构建。 相反,最好依赖生成的报告,并跟踪不同场景下评估分数随时间的总体趋势(只有在多个不同测试的评估分数大幅下降时,才能使单个构建失败)。 也就是说,这里有一些细微差别,选择是否验证单个结果,具体取决于具体的用例。
当该方法返回时,
scenarioRun对象被释放,评估结果将存储到在s_defaultReportingConfiguration中配置的基于磁盘的结果存储中。
运行测试/评估
使用首选测试工作流运行测试,例如,使用 CLI 命令 dotnet test 或通过 测试资源管理器运行测试。
生成报表
通过从终端窗口中运行以下命令 ,安装 Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Console .NET 工具:
dotnet tool install --local Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Evaluation.Console运行以下命令生成报表:
dotnet tool run aieval report --path <path\to\your\cache\storage> --output report.html打开
report.html文件。 结果应该如下所示。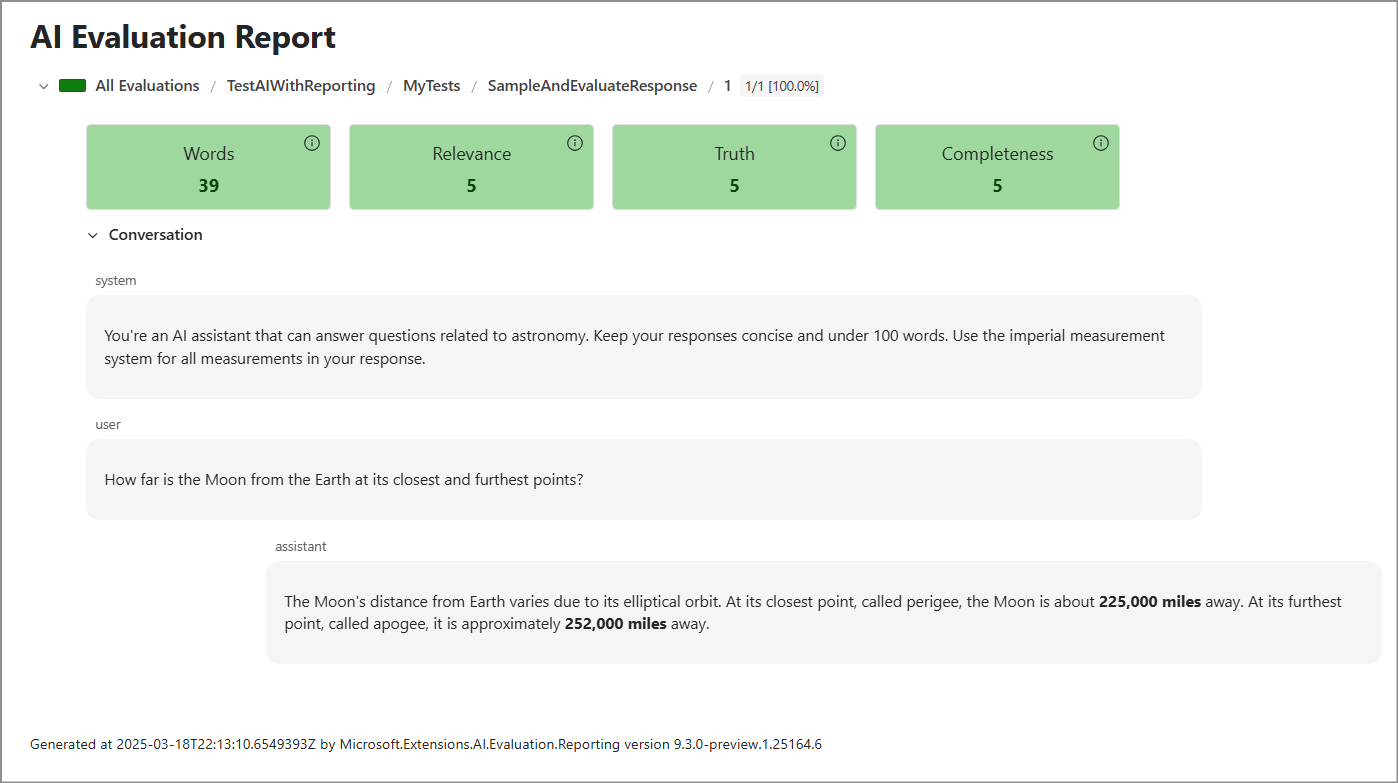
后续步骤
- 导航到存储测试结果的目录(即
C:\TestReports,除非在创建 ReportingConfiguration时修改了位置)。 在results子目录中,请注意,每个测试运行都有一个文件夹,其名称为时间戳(ExecutionName)。 其中每个文件夹都是每个方案名称的文件夹,在本例中,只需项目中的单个测试方法即可。 该文件夹包含包含所有数据(包括消息、响应和评估结果)的 JSON 文件。 - 扩展评估。 以下是几个想法:
- 添加其他自定义计算器,例如 使用 AI 来确定响应中使用的度量系统 。
- 添加另一个测试方法,例如,一种评估来自 LLM 的多个响应的方法。 由于每个响应可能有所不同,因此最好对问题至少进行一些回复采样和评估。 在这种情况下,每次调用 CreateScenarioRunAsync(String, String, IEnumerable<String>, IEnumerable<String>, CancellationToken)时,都会指定迭代名称。
