适用于:✔️ Linux VM ✔️ 灵活规模集
在前面的教程中,你已学习如何通过 SSH 连接到虚拟机 (VM) 并手动安装 NGINX。 若要以快速一致的方式创建 VM,通常需要某种形式的自动化。 在首次启动 VM 时实现自定义的常见方法是使用 cloud-init。 本教程介绍如何执行下列操作:
- 创建 cloud-init 配置文件
- 创建使用 cloud-init 文件的 VM
- 在创建 VM 后,查看正在运行的 Node.js 应用
- 使用 Key Vault 安全地存储证书
- 使用 cloud-init 自动进行 NGINX 的安全部署
如果选择在本地安装并使用 CLI,本教程要求运行 Azure CLI 2.0.30 或更高版本。 运行 az --version 即可查找版本。 如果需要进行安装或升级,请参阅安装 Azure CLI。
Cloud-init 概述
Cloud-init 是一种广泛使用的方法,用于在首次启动 Linux VM 时对其进行自定义。 可使用 cloud-init 来安装程序包和写入文件,或者配置用户和安全性。 在初始启动期间运行 cloud-init 时,无需额外的步骤且无需代理来应用配置。
Cloud-init 还支持不同的发行版。 例如,不要使用 apt-get 安装或 yum 安装来安装包。 可定义要安装的程序包的列表。 Cloud-init 将为所选发行版自动使用本机包管理工具。
我们正在与合作伙伴协作,将 cloud-init 纳入用户向 Azure 提供的映像中并使其在映像中正常运行。 有关每个发行版的 cloud-init 支持的详细信息,请参阅 Azure 中 VM 的 Cloud-init 支持。
创建 cloud-init 配置文件
若要运行 cloud-init,请创建一个 VM,以便安装 NGINX 并运行简单的“Hello World”Node.js 应用。 以下 cloud-init 配置安装所需的包,创建 Node.js 应用,然后初始化并启动应用。
在 bash 提示符下或在 Cloud Shell 中,创建名为 cloud-init.txt 的文件并粘贴以下配置。 例如,键入 sensible-editor cloud-init.txt 以创建文件并查看可用编辑器的列表。 请确保已正确复制整个 cloud-init 文件,尤其是第一行:
#cloud-config
package_upgrade: true
packages:
- nginx
- nodejs
- npm
write_files:
- owner: www-data:www-data
path: /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
defer: true
content: |
server {
listen 80;
___location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection keep-alive;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
- owner: azureuser:azureuser
path: /home/azureuser/myapp/index.js
defer: true
content: |
var express = require('express')
var app = express()
var os = require('os');
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello World from host ' + os.hostname() + '!')
})
app.listen(3000, function () {
console.log('Hello world app listening on port 3000!')
})
runcmd:
- service nginx restart
- cd "/home/azureuser/myapp"
- npm init
- npm install express -y
- nodejs index.js
有关 cloud-init 配置选项的详细信息,请参阅 cloud-init 配置示例。
创建虚拟机
使用 az group create 创建资源组,才能创建 VM。 以下示例创建了一个资源组。 在这些命令中,随机后缀追加到资源组和 VM 名称,以防止在重复部署期间发生名称冲突。
export RANDOM_SUFFIX=$(openssl rand -hex 3)
export RESOURCE_GROUP="myResourceGroupAutomate$RANDOM_SUFFIX"
export REGION="eastus2"
az group create --name $RESOURCE_GROUP --___location $REGION
结果:
{
"id": "/subscriptions/xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx/resourceGroups/myResourceGroupAutomatexxx",
"___location": "eastus",
"managedBy": null,
"name": "myResourceGroupAutomatexxx",
"properties": {
"provisioningState": "Succeeded"
},
"tags": null,
"type": "Microsoft.Resources/resourceGroups"
}
现使用 az vm create 创建 VM。 使用 --custom-data 参数传递到 cloud-init 配置文件中。 如果未将 cloud-init.txt 配置文件保存在现有工作目录中,请提供该文件的完整路径。 以下示例创建 VM;请注意,VM 名称还追加了随机后缀。
export VM_NAME="myAutomatedVM$RANDOM_SUFFIX"
az vm create \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--name $VM_NAME \
--image Ubuntu2204 \
--admin-username azureuser \
--generate-ssh-keys \
--custom-data cloud-init.txt
结果:
{
"fqdns": "",
"id": "/subscriptions/xxxxx/resourceGroups/myResourceGroupAutomatexxx/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/myAutomatedVMxxx",
"___location": "eastus",
"name": "myAutomatedVMxxx",
"powerState": "VM running",
"publicIpAddress": "x.x.x.x",
"resourceGroup": "myResourceGroupAutomatexxx",
"zones": ""
}
创建 VM、安装程序包和启动应用需耗时几分钟。 在 Azure CLI 向你返回提示之后,仍然存在继续运行的后台任务。 可能还需等待几分钟才能访问应用。 创建 VM 后,请记下 Azure CLI 显示的 publicIpAddress。 此地址用于通过 Web 浏览器访问 Node.js 应用。
若要使 VM 能使用 Web 流量,请通过 az vm open-port 从 Internet 打开端口 80:
az vm open-port --port 80 --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $VM_NAME
结果:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"name": "80",
"protocol": "tcp",
"publicPort": 80,
"privatePort": 80
}
],
"id": "/subscriptions/xxxxx/resourceGroups/myResourceGroupAutomatexxx/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/myAutomatedVMxxx",
"___location": "eastus",
"name": "myAutomatedVMxxx"
}
测试 Web 应用
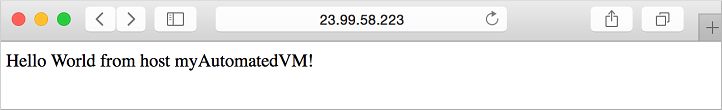
现在,可以打开 Web 浏览器并在地址栏中输入公共 IP 地址。 在 VM 创建过程中提供自己的公共 IP 地址。 将显示 Node.js 应用,如下例所示:
后续步骤
在本教程中,你使用 cloud-init 在首次启动时配置了 VM。 你已了解如何执行以下操作:
- 创建 cloud-init 配置文件
- 创建使用 cloud-init 文件的 VM
- 在创建 VM 后,查看正在运行的 Node.js 应用
- 使用 Key Vault 安全地存储证书
- 使用 cloud-init 自动进行 NGINX 的安全部署
转到下一教程,了解如何创建自定义 VM 映像。