Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra is a fully managed service for pure open-source Apache Cassandra clusters. The service also allows configurations to be overridden, depending on the specific needs of each workload, which allows maximum flexibility and control where needed.
This quickstart demonstrates how to use the Azure portal to create an Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra cluster.
Prerequisites
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Create a managed instance cluster
Sign in to the Azure portal.
From the search bar, search for Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra and select the result.
Select Create Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra cluster.
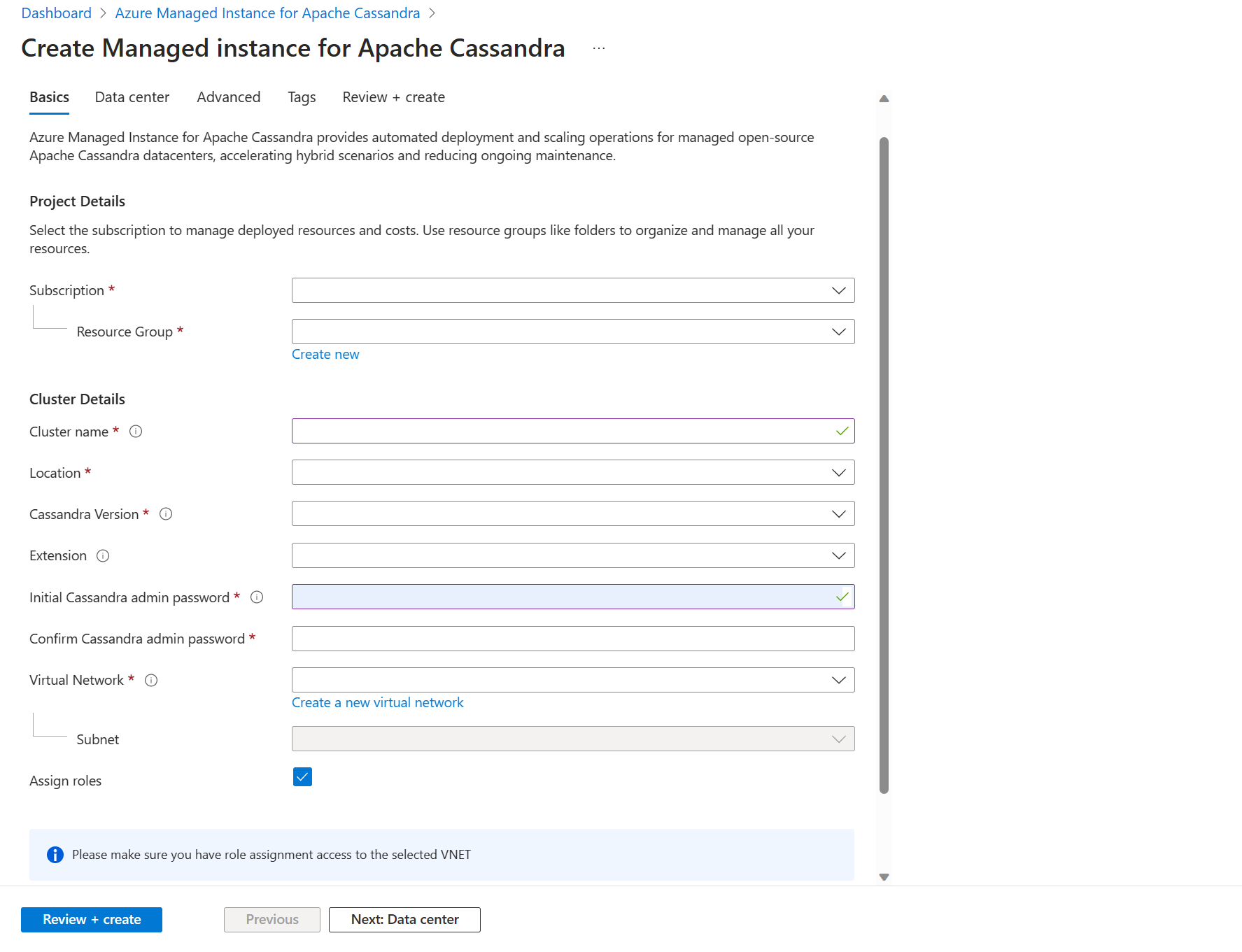
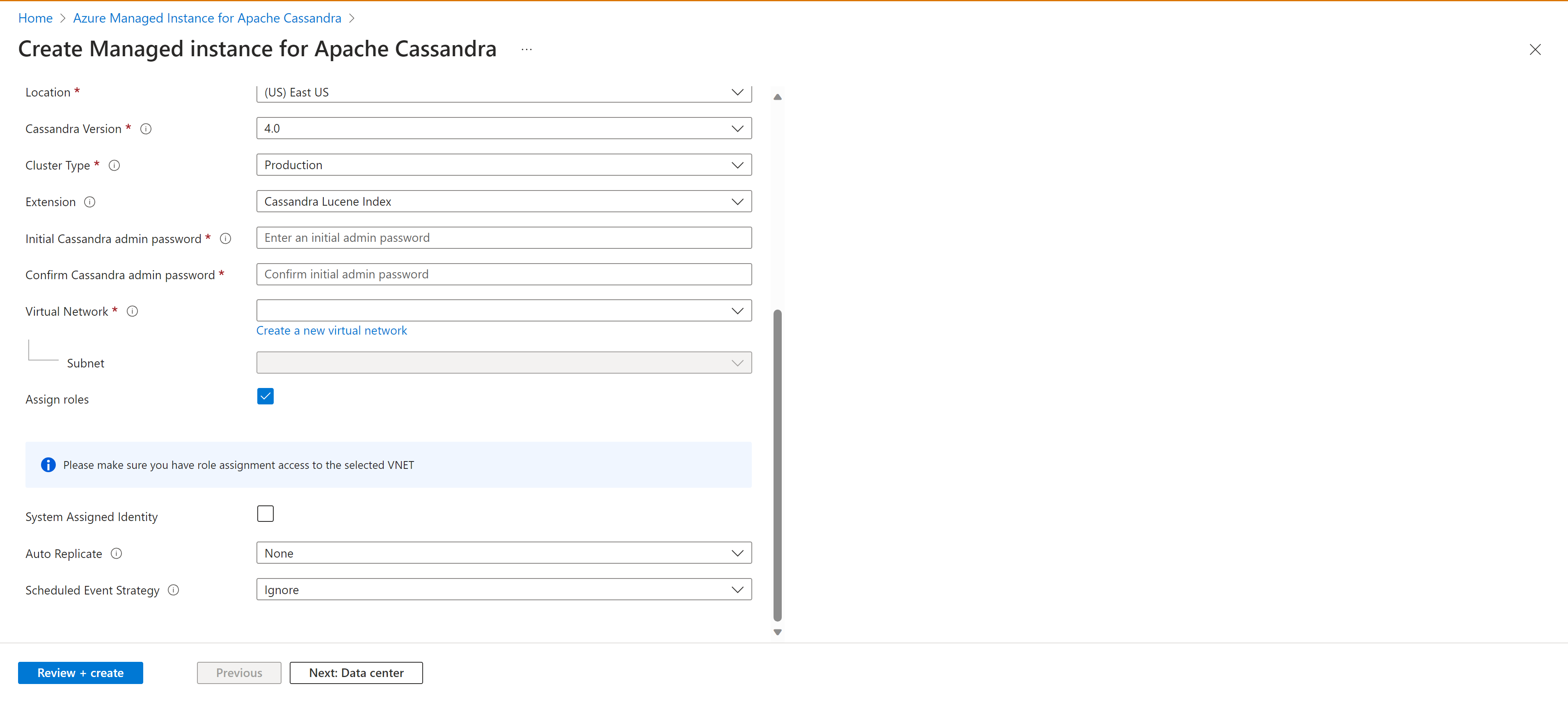
From the Create Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra pane, enter the following details:
- Subscription - From the dropdown, select your Azure subscription.
- Resource Group- Specify whether you want to create a new resource group or use an existing one. A resource group is a container that holds related resources for an Azure solution.
- Cluster name - Enter a name for your cluster.
- Location - Location to deploy the cluster.
- Cassandra version - Version of Apache Cassandra to deploy.
- Extention - Extensions to add, including Cassandra Lucene Index.
- Initial Cassandra admin password - Password that is used to create the cluster.
- Confirm Cassandra admin password - Reenter your password.
- Virtual Network - Select an exiting virtual network and subnet, or create a new one.
- Assign roles - Virtual networks require special permissions to allow managed Cassandra clusters to be deployed. Keep this box checked if you're creating a new virtual network, or using an existing virtual network without permissions applied. If you use a virtual network where you previously deployed Azure SQL Managed Instance Cassandra clusters, unselect this option.
Tip
If you use VPN, you don't need to open another connection.
Note
The Deployment of an Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra requires internet access. Deployment fails in environments where internet access is restricted. Make sure you aren't blocking access in your virtual network to the following vital Azure services that are necessary for Managed Cassandra to work properly. For more information, see Required outbound network rules.
- Azure Storage
- Azure KeyVault
- Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets
- Azure Monitoring
- Microsoft Entra ID
- Azure Security
- Auto Replicate. Choose the form of autoreplication to use. For more information, see Turnkey replication.
- Schedule Event Strategy. The strategy use by the cluster for scheduled events.
Tip
- StopANY means stop any node when there's a scheduled event for the node.
- StopByRack means only stop node in a given rack for a given Scheduled Event. For instance, if several events are scheduled for nodes in different racks at the same time, only nodes in one rack stop. Other nodes in other racks are delayed.
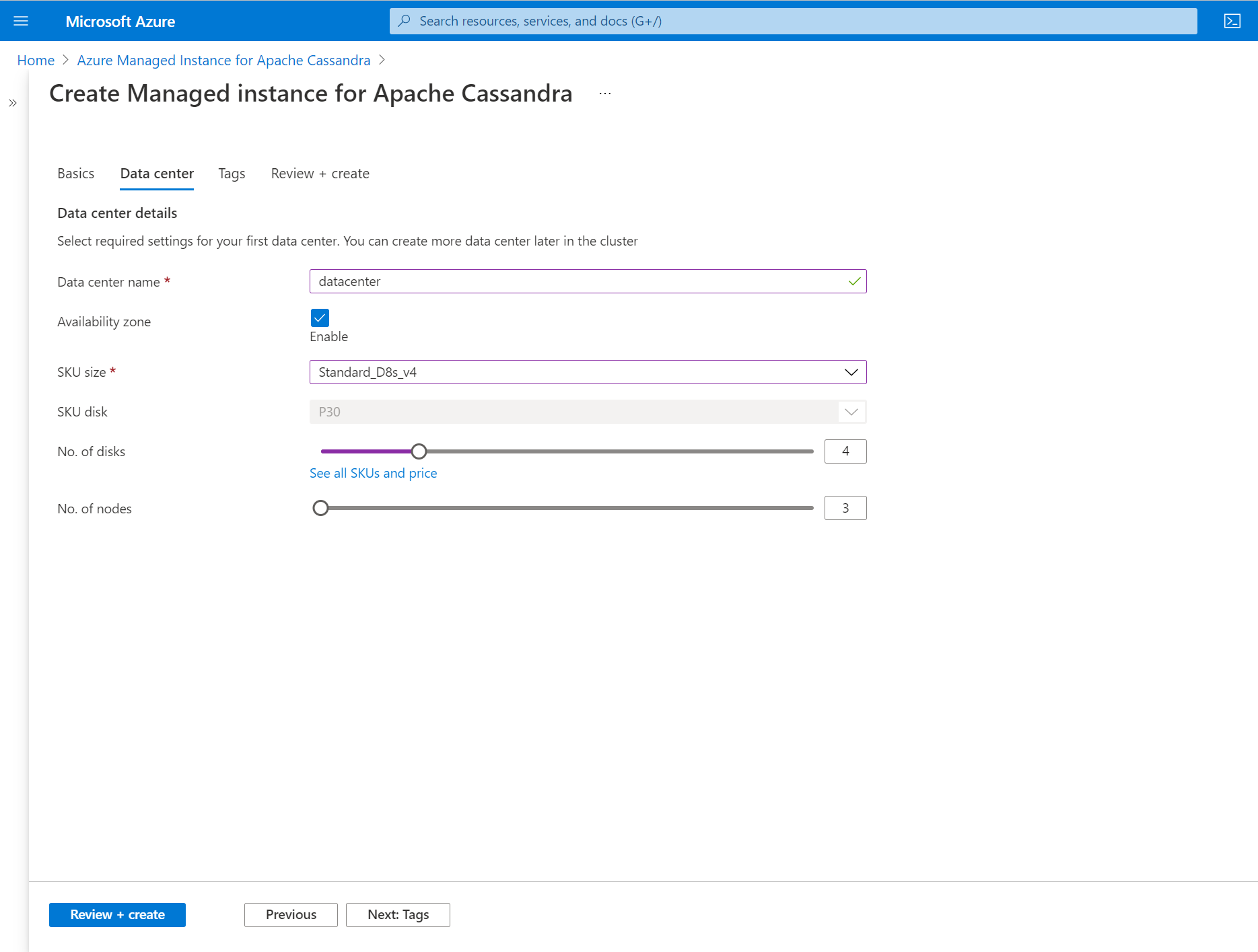
Next select the Data center tab.
Enter the following details:
- Data center name. Type a data center name in the text field.
- Availability zone. Check this box if you want availability zones to be enabled.
- SKU Size. Choose from the available virtual machine SKU sizes.
Note
We introduced write-through caching (Public Preview) by using L-series VM SKUs. This implementation aims to minimize tail latencies and enhance read performance, particularly for read intensive workloads. These specific SKUs are equipped with locally attached disks, which ensure hugely increased IOPS for read operations and reduced tail latency.
Important
Write-through caching is in public preview. This feature is provided without a service level agreement. We don't recommend it for production workloads. For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
- No. of disks. Choose the number of p30 disks to be attached to each Cassandra node.
- No. of nodes. Choose the number of Cassandra nodes to deploy to this datacenter.
Warning
Availability zones aren't supported in all regions. Deployments fail if you select a region where availability zones aren't supported. For more information, see Azure regions list.
The successful deployment of availability zones is also subject to the availability of compute resources in all of the zones in the given region. Deployments might fail if the SKU you selected, or capacity, isn't available across all zones.
Next, select Review + create > Create.
Note
It can take up to 15 minutes to create a cluster.
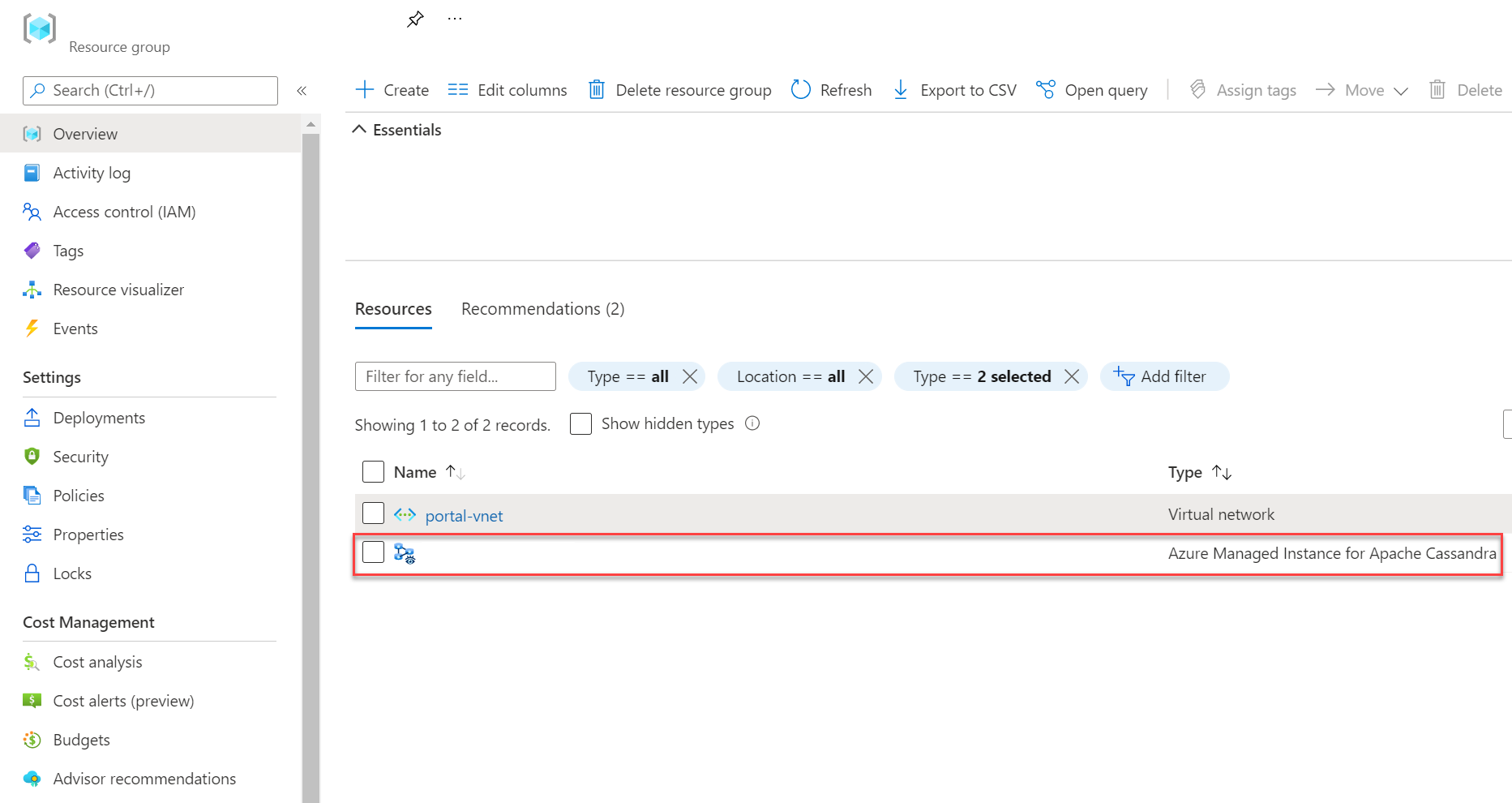
After the deployment finishes, check your resource group to see the newly created managed instance cluster:
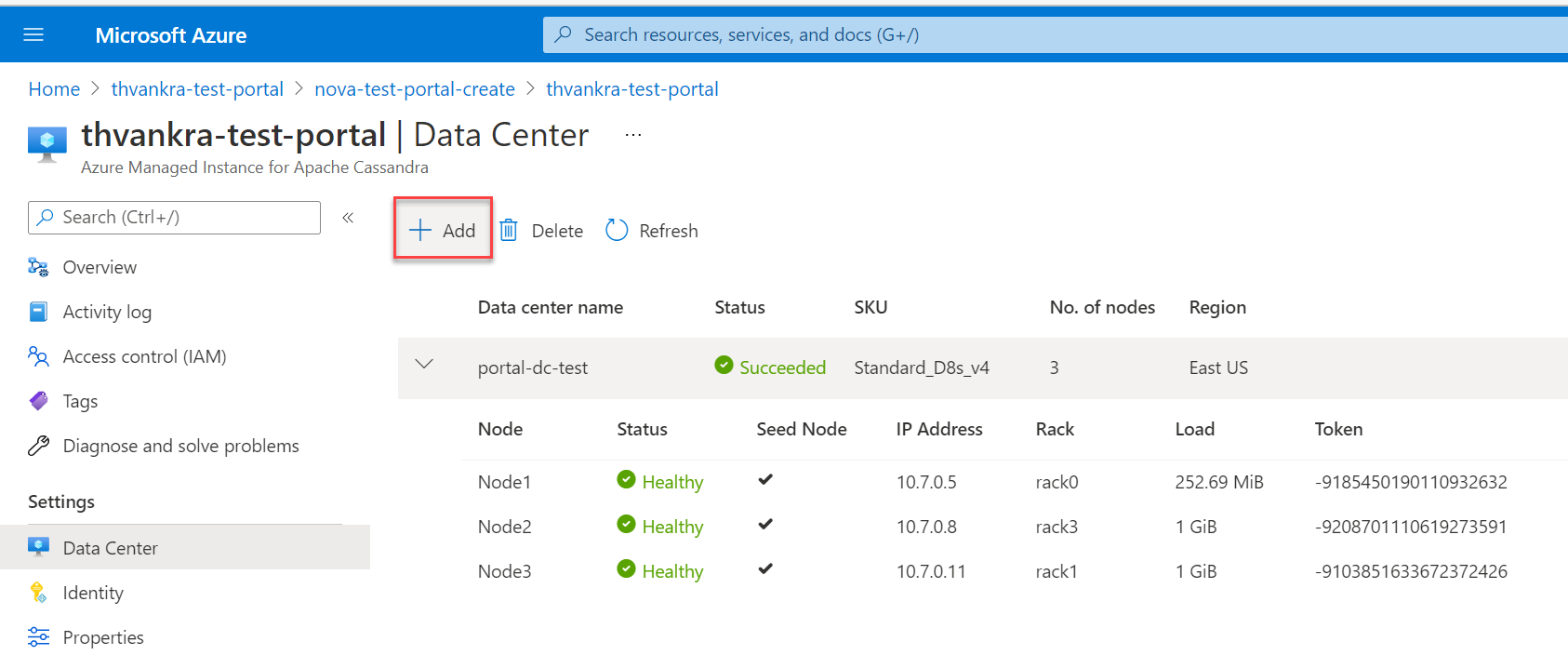
To browse through the cluster nodes, navigate to the cluster resource and open the Data Center pane:
Scale a datacenter
Now that you deployed a cluster with a single data center, you can scale horizontally or vertically by highlighting the data center, and selecting the Scale button:
Horizontal scale
To scale out or scale in on nodes, move the slider to the desired number, or just edit the value. When finished, select Scale.
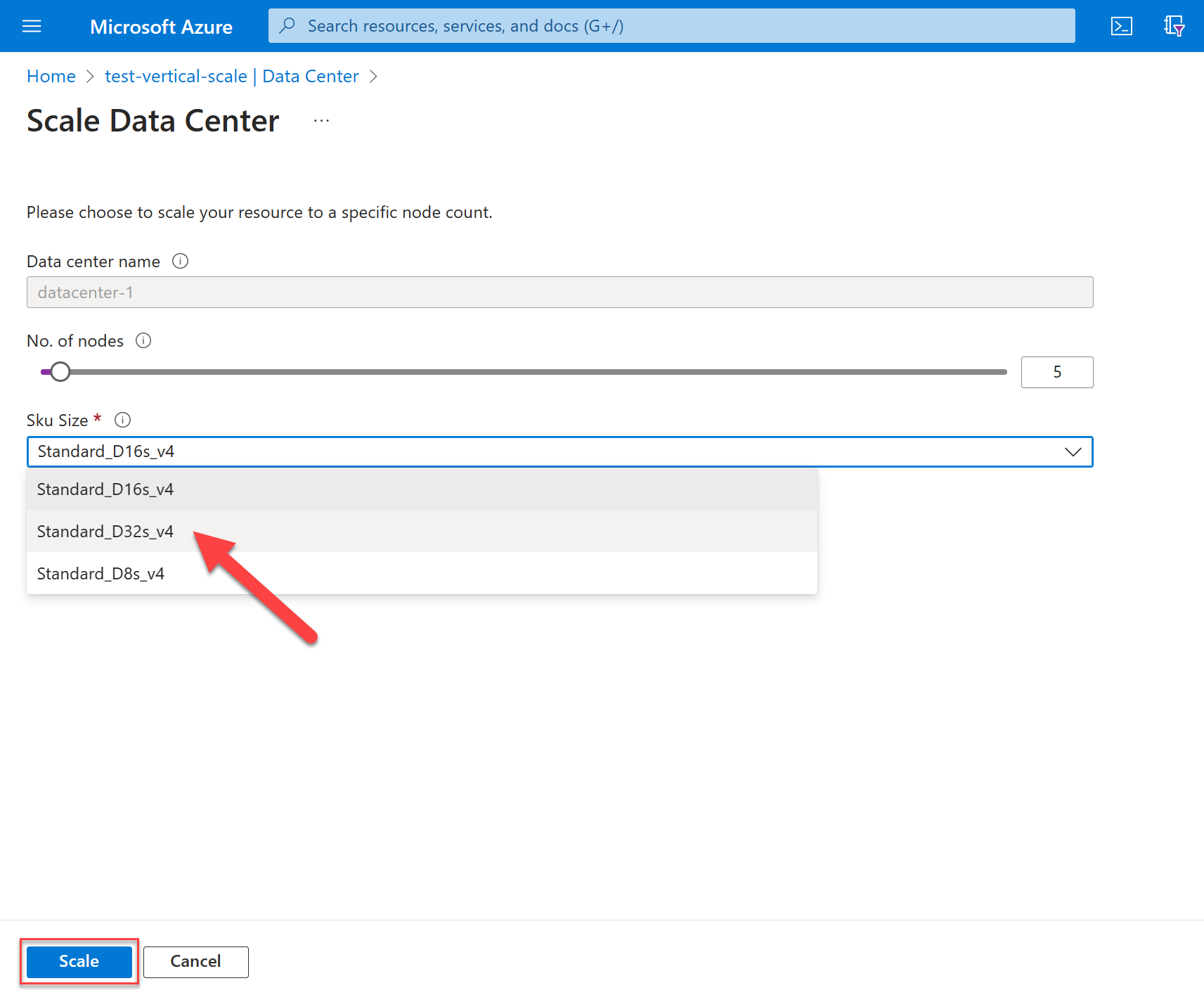
Vertical scale
To scale up or to scale down SKU size for your nodes, select from Sku Size. When finished, select Scale.
Note
The length of time it takes for a scaling operation depends on various factors. It might take several minutes. When Azure notifies you that the scale operation completed, it doesn't mean that all your nodes joined the Cassandra ring. Nodes are fully commissioned when they all display a status of healthy and the datacenter status reads succeeded.
Scaling is an online operation and works in the same manner as described for patching. For more information, see Patching.
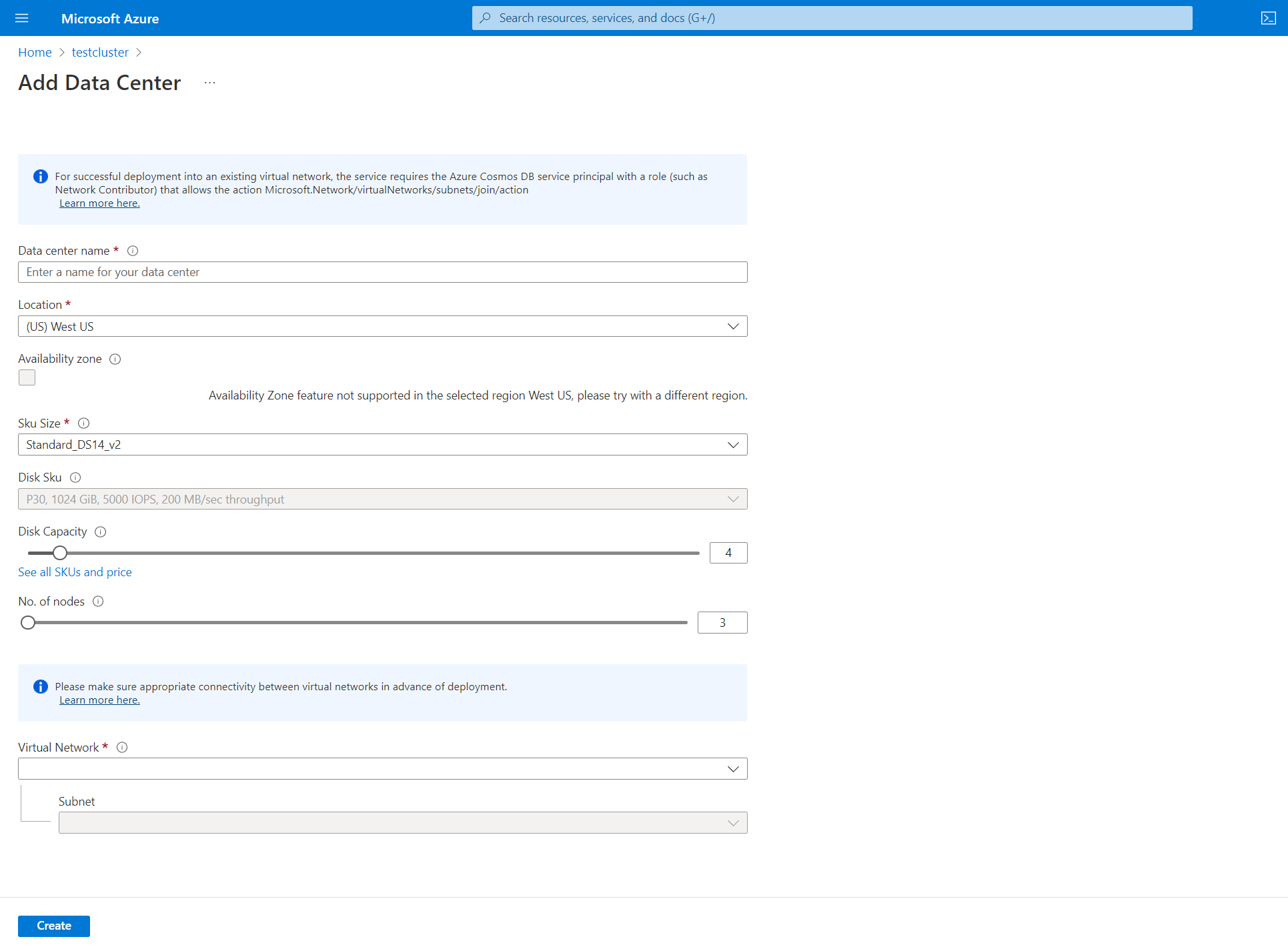
Add a datacenter
To add another datacenter, select the add button in the Data Center pane:
Warning
If you're adding a datacenter in a different region, you need to select a different virtual network. You also need to ensure that this virtual network has connectivity to the primary region's virtual network created previously. Also, make sure that any other virtual networks that are hosting datacenters within the managed instance cluster. For more information, see Connect virtual networks with virtual network peering.
You also need to make sure that you applied the appropriate role to your virtual network before you attempt to deploy a managed instance cluster, using the following CLI command.
az role assignment create \ --assignee a232010e-820c-4083-83bb-3ace5fc29d0b \ --role 4d97b98b-1d4f-4787-a291-c67834d212e7 \ --scope /subscriptions/<subscriptionID>/resourceGroups/<resourceGroupName>/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/<vnetName>Fill in the appropriate fields:
- Datacenter name. From the dropdown list, select your Azure subscription.
- Availability zone. Select if you want availability zones to be enabled in this datacenter.
- Location. Location where your datacenter is deployed.
- SKU Size. Choose from the available virtual machine SKU sizes.
- No. of disks. Choose the number of p30 disks to be attached to each Cassandra node.
- No. of nodes. Choose the number of Cassandra nodes to deploy to this datacenter.
- Virtual Network. Select an exiting virtual network and subnet.
Warning
The Azure portal doesn't allow creation of a new virtual network when you add a datacenter. You need to choose an existing virtual network and you need to ensure there's connectivity between the target subnets where datacenters are deployed. You also need to apply the appropriate role to the virtual network to allow deployment, as described previously.
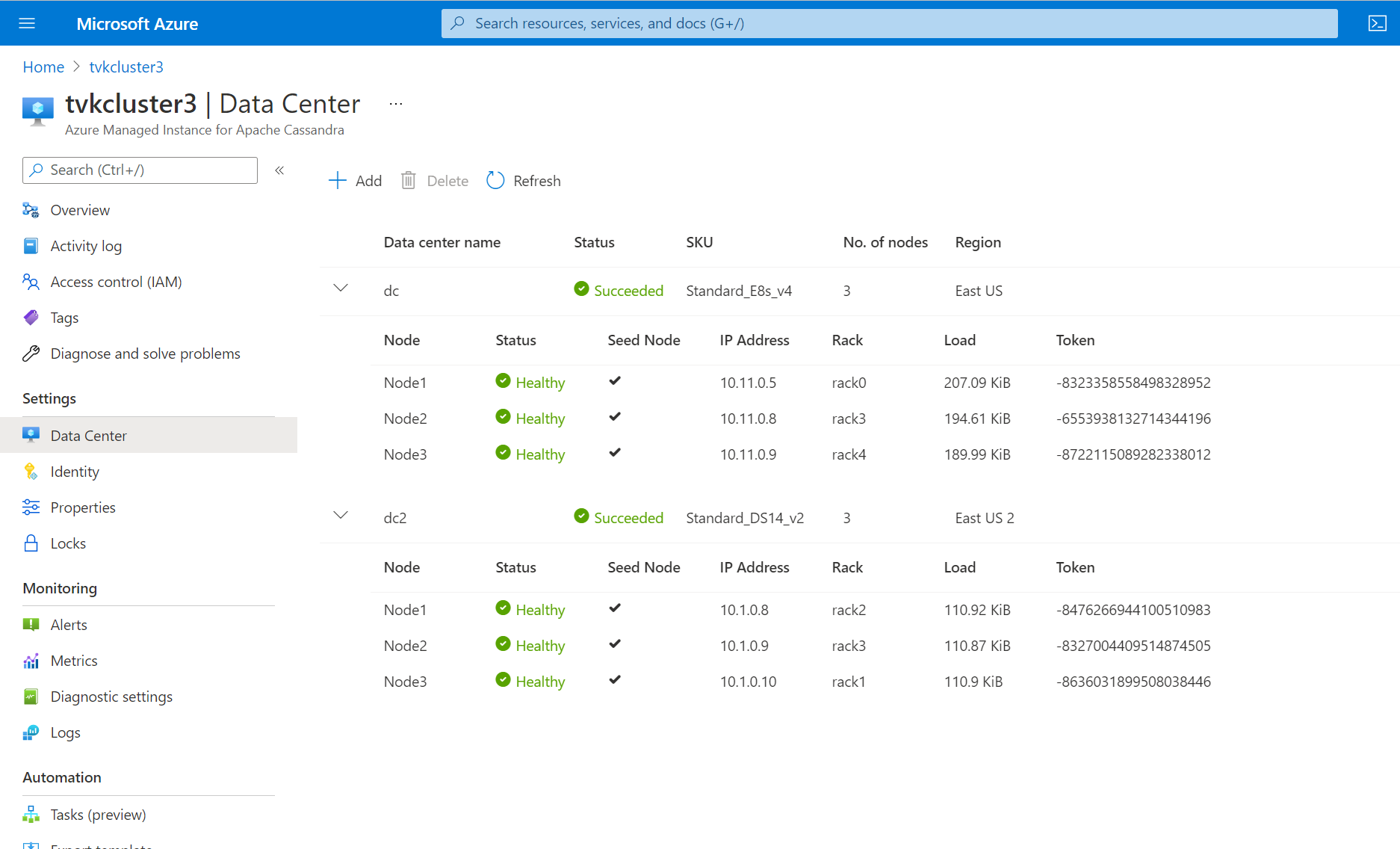
When the datacenter is deployed, you should be able to view all datacenter information in the Data Center pane:
To ensure replication between data centers, connect to cqlsh and use the following CQL query to update the replication strategy in each keyspace to include all datacenters across the cluster. System tables are updated automatically.
ALTER KEYSPACE "ks" WITH REPLICATION = {'class': 'NetworkTopologyStrategy', 'dc': 3, 'dc2': 3};If you're adding a data center to a cluster where there's already data, run
rebuildto replicate the historical data. In Azure CLI, use the following command runnodetool rebuildon each node of the new data center. This action replaces<new dc ip address>with the IP address of the node, and<olddc>with the name of your existing data center:az managed-cassandra cluster invoke-command \ --resource-group $resourceGroupName \ --cluster-name $clusterName \ --host <new dc ip address> \ --command-name nodetool --arguments rebuild="" "<olddc>"=""Warning
You should not allow application clients to write to the new data center until you apply keyspace replication changes. Otherwise, rebuild doesn't work, and you need to create a support request so our team can run
repairon your behalf.
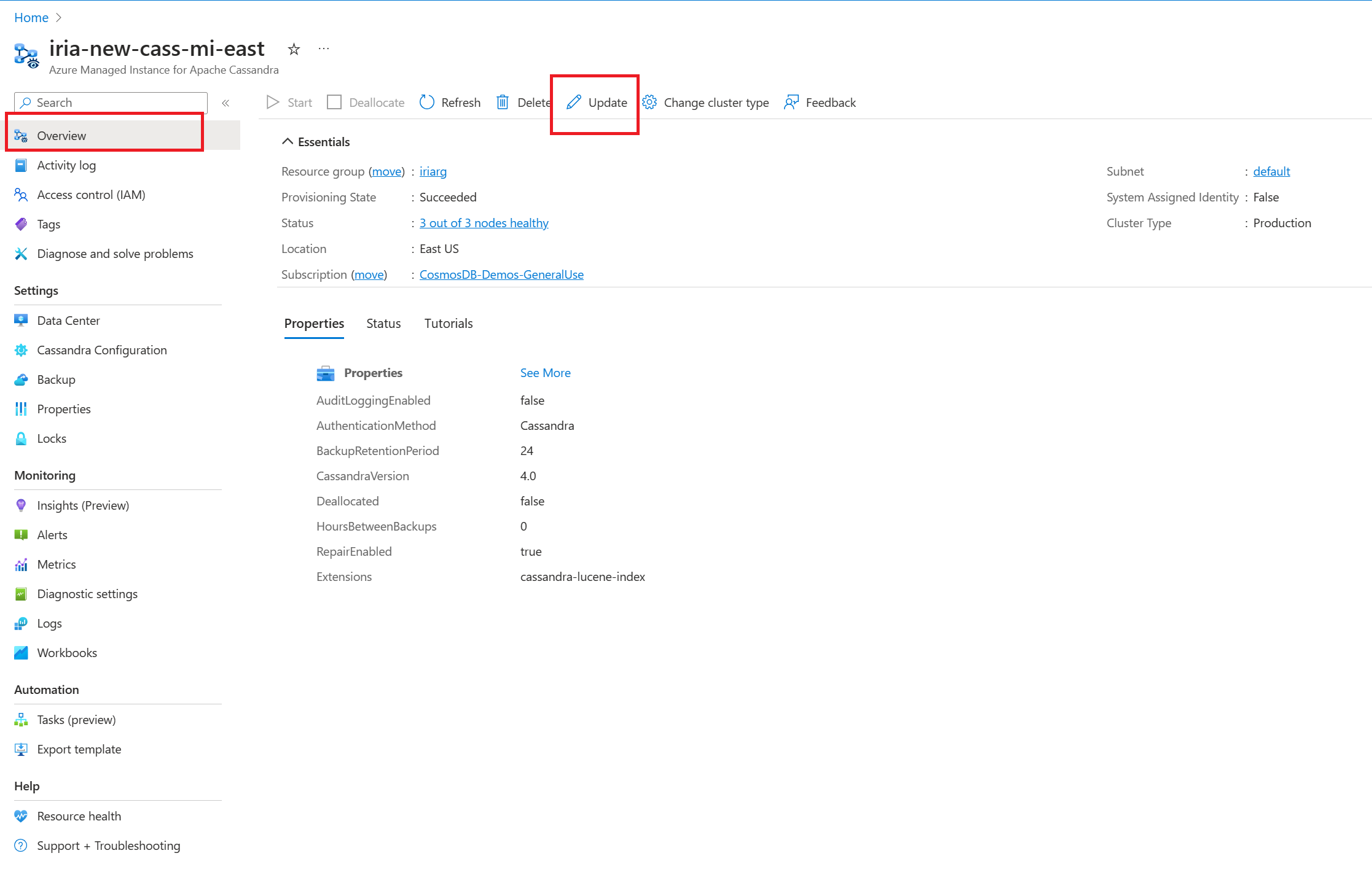
Update Cassandra configuration
The service allows updates to Cassandra YAML configuration on a datacenter by using the Azure portal or by using CLI commands. To update settings in the portal:
Find
Cassandra Configurationunder settings. Highlight the data center whose configuration you want to change, and select update:In the window that opens, enter the field names in YAML format, as shown here. Then select update.
When update is complete, the overridden values appear in the
Cassandra Configurationpane:Note
Only overridden Cassandra configuration values are shown in the Azure portal.
Important
Ensure the Cassandra yaml settings you provide are appropriate for the version of Cassandra you deployed. See Cassandra v3.11 for Cassandra v3.11 settings and Cassandra v4.0 for v4.0. You can't update the following YAML settings:
- cluster_name
- seed_provider
- initial_token
- autobootstrap
- client_encryption_options
- server_encryption_options
- transparent_data_encryption_options
- audit_logging_options
- authenticator
- authorizer
- role_manager
- storage_port
- ssl_storage_port
- native_transport_port
- native_transport_port_ssl
- listen_address
- listen_interface
- broadcast_address
- hints_directory
- data_file_directories
- commitlog_directory
- cdc_raw_directory
- saved_caches_directory
- endpoint_snitch
- partitioner
- rpc_address
- rpc_interface
Update Cassandra version
Important
Cassandra 5.0 and Turnkey Version Updates, are in public preview. These features are provided without a service level agreement. We don't recommend these features for production workloads. For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
You can conduct in-place major version upgrades directly from the portal or through Az CLI, Terraform, or ARM templates.
Find the
Updatepanel from the Overview tab.Select the Cassandra version from the dropdown list.
Warning
Don't skip versions. We recommend updating only from one version to another example 3.11 to 4.0, 4.0 to 4.1.
Select update to save.
Turnkey replication
Cassandra 5.0 introduces a streamlined approach for deploying multi-region clusters, offering enhanced convenience and efficiency. If you use turnkey replication functionality, setting up and managing multi-region clusters becomes more accessible, allowing for smoother integration and operation across distributed environments.
This update significantly reduces the complexities associated with deploying and maintaining multiple region configurations, allowing users to use Cassandra's capabilities with greater ease and effectiveness.
Tip
- None: Auto replicate is set to none.
- SystemKeyspaces: Autoreplicate all system keyspaces (system_auth, system_traces, system_auth).
- AllKeyspaces: Autoreplicate all keyspaces and monitor if new keyspaces are created and then apply autoreplicate settings automatically.
Autoreplication scenarios
- When you add a new data center, the autoreplicate feature in Cassandra seamlessly runs
nodetool rebuildto ensure the successful replication of data across the added data center. - Removing a data center triggers an automatic removal of the specific data center from the keyspaces.
For external data centers, such as those hosted on-premises, they can be included in the keyspaces by using the external data center property. This approach enables Cassandra to incorporate these external data centers as sources for the rebuilding process.
Warning
Setting autoreplicate to AllKeyspaces changes your keyspaces replication to include:
WITH REPLICATION = { 'class' : 'NetworkTopologyStrategy', 'on-prem-datacenter-1' : 3, 'mi-datacenter-1': 3 }
If this topology isn't what you want, use SystemKeyspaces, adjust them yourself, and run nodetool rebuild manually on the Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra cluster.
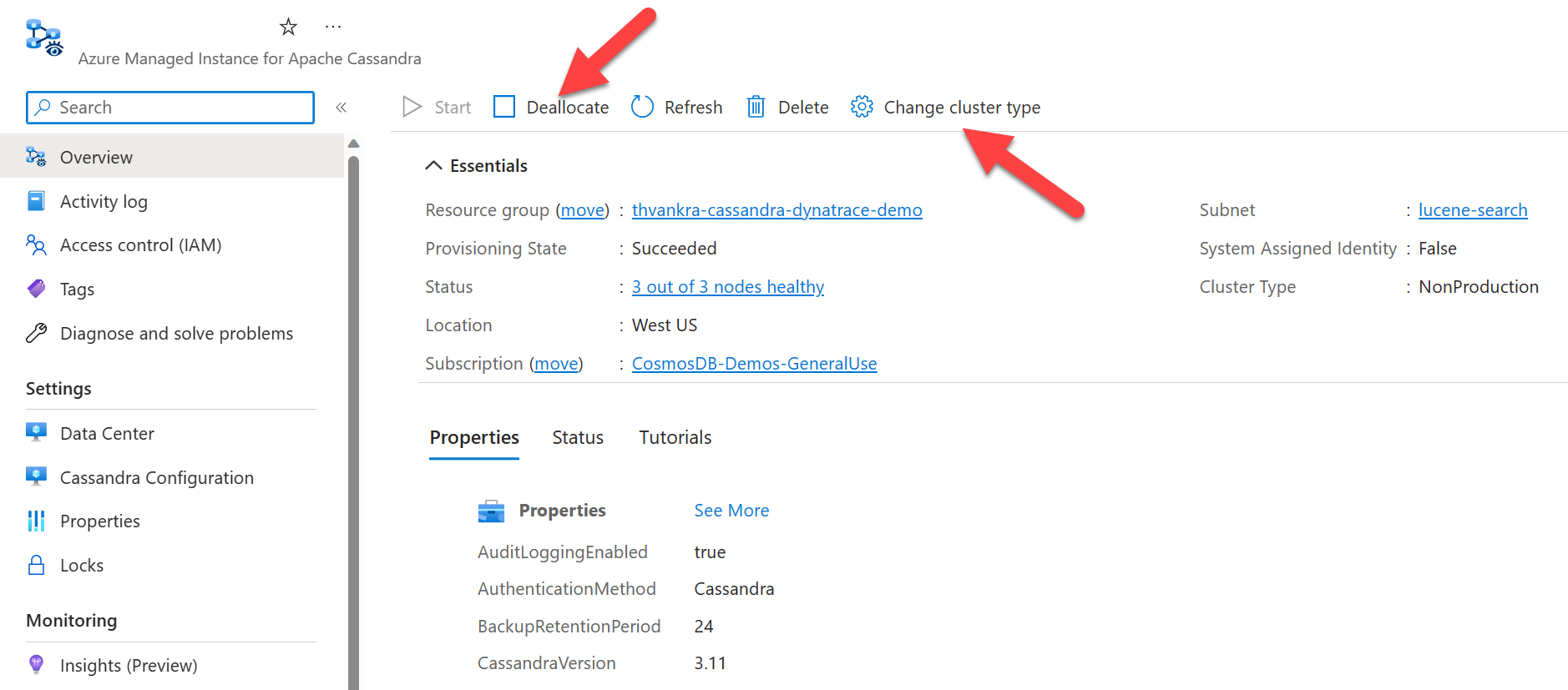
Deallocate cluster
For nonproduction environments, you can pause or deallocate resources in the cluster in order to avoid being charged for them. You continue to be charged for storage. First change cluster type to NonProduction, then deallocate.
Tip
Cluster type should be used as "Non-Production" only to save development costs. They might come with smaller SKUs, and should NOT be used to run production workloads.
Warning
- Cluster type defined as "Nonproduction" don't have SLA guarantees applied to it.
- Don't run any schema or write operations during deallocation. This action can lead to data loss and in rare cases schema corruption requiring manual intervention from the support team.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter an error when applying permissions to your virtual network using Azure CLI, you can apply the same permission manually from the Azure portal. An example of such an error is Cannot find user or service principal in graph database for 'e5007d2c-4b13-4a74-9b6a-605d99f03501'. For more information, see Use the Azure portal to add Azure Cosmos DB service principal.
Note
The Azure Cosmos DB role assignment is used for deployment purposes only. Azure Managed Instanced for Apache Cassandra has no backend dependencies on Azure Cosmos DB.
Connecting to your cluster
Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra doesn't create nodes with public IP addresses. To connect to your newly created Cassandra cluster, create another resource inside the virtual network. This resource could be an application, or a virtual machine with Apache's open-source query tool CQLSH installed. You can use a template to deploy an Ubuntu virtual machine.
Connecting from CQLSH
After the virtual machine is deployed, use SSH to connect to the machine, and install CQLSH using the below commands:
# Install default-jre and default-jdk
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk openjdk-8-jre
# Install the Cassandra libraries in order to get CQLSH:
echo "deb http://archive.apache.org/dist/cassandra/debian 311x main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cassandra.sources.list
curl https://downloads.apache.org/cassandra/KEYS | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install cassandra
# Export the SSL variables:
export SSL_VERSION=TLSv1_2
export SSL_VALIDATE=false
# Connect to CQLSH (replace <IP> with the private IP addresses of a node in your Datacenter):
host=("<IP>")
initial_admin_password="Password provided when creating the cluster"
cqlsh $host 9042 -u cassandra -p $initial_admin_password --ssl
Connecting from an application
As with CQLSH, connecting from an application using one of the supported Apache Cassandra client drivers requires SSL encryption to be enabled, and certification verification to be disabled. See samples for connecting to Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra using Java, .NET, Node.js, and Python.
We recommend disabling certificate verification because certificate verification doesn't work unless you map IP addresses of your cluster nodes to the appropriate ___domain. If you have an internal policy which mandates that you do SSL certificate verification for any application, you can facilitate this setup by adding entries like 10.0.1.5 host1.managedcassandra.cosmos.azure.com in your hosts file for each node. If you take this approach, you also need to add new entries whenever scaling up nodes.
For Java, we also highly recommend enabling speculative execution policy where applications are sensitive to tail latency. For a demo that illustrates how this approach works, see and how to enable the policy Demo: implementing speculative execution.
Note
In most cases, it should not be necessary to configure or install certificates (such as rootCA, node, or client, truststores) to connect to Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra. SSL encryption can be enabled by using the default truststore and password of the runtime being used by the client because Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra certificates are trusted by that environment. In rare cases, if the certificate isn't trusted, you might need to add it to the truststore. See Java, .NET, Node.js, and Python.
Configuring client certificates (optional)
Configuring client certificates is optional. A client application can connect to Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra as long as the preceding steps are completed. However, if you prefer, you can also create and configure client certificates for authentication. In general, there are two ways of creating certificates:
- Self signed certs. A private and public (no CA) certificate for each node. In this case, you need all public certificates.
- Certs signed by a CA. This certificate can be a self-signed CA or even a public one. In this case, you need the root CA certificate and all intermediaries (if applicable). For more information, see Preparing SSL certificates for production.
If you want to implement client-to-node certificate authentication or mutual Transport Layer Security (mTLS), provide the certificates by using Azure CLI. The following command uploads and applies your client certificates to the truststore for the managed instance cluster. You don't need to edit cassandra.yaml settings. After you apply the command, your cluster requires Cassandra to verify the certificates when a client connects. See require_client_auth: true in Cassandra client_encryption_options.
resourceGroupName='<Resource_Group_Name>'
clusterName='<Cluster Name>'
az managed-cassandra cluster update \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--cluster-name $clusterName \
--client-certificates /usr/csuser/clouddrive/rootCert.pem /usr/csuser/clouddrive/intermediateCert.pem
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use this managed instance cluster, delete it with the following steps:
- From the left-hand menu of Azure portal, select Resource groups.
- From the list, select the resource group you created for this quickstart.
- On the resource group Overview pane, select Delete resource group.
- In the next window, enter the name of the resource group to delete, and then select Delete.